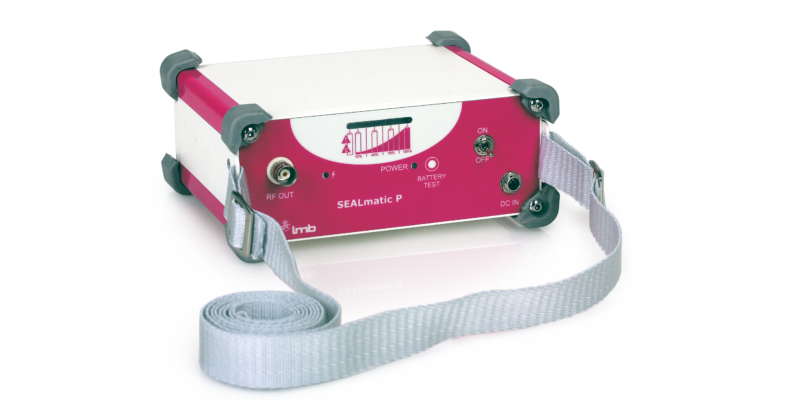
A blood tube sealer is used to seal a blood bag to prevent blood leakage and hemolysis. They are also used to keep blood collection tubes, infusion bags, blood bags, and other PVC medical grade tubings secure. Blood tube sealers are also widely used in component and reference laboratories such as blood banks and hospitals.
A blood tube sealer is also used in many biological industries to ensure leakage-free and large scale sealing. There are various types of blood tube sealers now available. Some of the most common include those with single and multi-clamps. Most also have a high-frequency dielectric heating system. It is used to seal blood bag tubes.
The Enticing Benefits of Blood Tube Sealers
Ideally, blood tube sealers will provide exceptional performance. However, they don’t have to cost a fortune. Hettich worked with experts to provide blood tube sealers that are top of the line and innovative but still affordable. Its benchtop tube sealer is one of the trusted segmenting and standalone tube sealers now available in the market.
Most benchtop blood tube sealers are designed for heavy-duty use. While benchtop blood tube sealers are not considered as mobile as their portable counterparts, they are considered more dependable in terms of performance. Choosing the right blood tube sealer can make a world of difference.
Constant movement can significantly affect the quality of the blood collected. During transport, it is also likely for body fluids to move inside the containers. Unfortunately, this can make them less ideal for research and study. They can also help ensure movement is minimized so the quality is preserved until it reaches its destination.
In addition, using a blood tube sealer can help ensure spillage is avoided and the specimen won’t go to waste. Moreover, it helps ensure the quality is preserved for better testing and analysis. Blood tube sealers can also help ensure that blood and other body fluids won’t coagulate.










Comments